Historical Evolution of NATO
NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, has played a pivotal role in shaping the geopolitical landscape of the post-World War II era. Its evolution over the decades has been marked by significant milestones and events.
The founding principles of NATO, enshrined in the North Atlantic Treaty signed in 1949, centered on collective defense and the preservation of peace and security among its member states. The organization was initially established as a response to the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union and its satellite states in Eastern Europe.
Founding and Early Years
In 1949, 12 countries—Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States—signed the North Atlantic Treaty, marking the official establishment of NATO. The treaty stipulated that an attack against one member state would be considered an attack against all, triggering a collective response.
Cold War Era
During the Cold War, NATO served as a bulwark against the Soviet Union and its Warsaw Pact allies. The organization played a crucial role in deterring Soviet aggression and maintaining stability in Western Europe. The Berlin Wall, built in 1961 to divide East and West Berlin, became a potent symbol of the ideological and political divide between NATO and the Soviet bloc.
Post-Cold War Era
With the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, NATO’s mission and objectives underwent significant re-evaluation. The organization expanded its membership to include former Warsaw Pact countries and adopted a more cooperative approach with Russia. NATO’s role in the post-Cold War era has focused on promoting stability and security in Europe, including through peacekeeping operations and partnerships with non-member states.
Recent Developments
In recent years, NATO has faced new challenges, including the rise of terrorism, cyber threats, and the annexation of Crimea by Russia. The organization has adapted to these challenges by strengthening its collective defense capabilities, enhancing intelligence sharing, and developing new strategies to counter emerging threats.
Membership and Structure of NATO
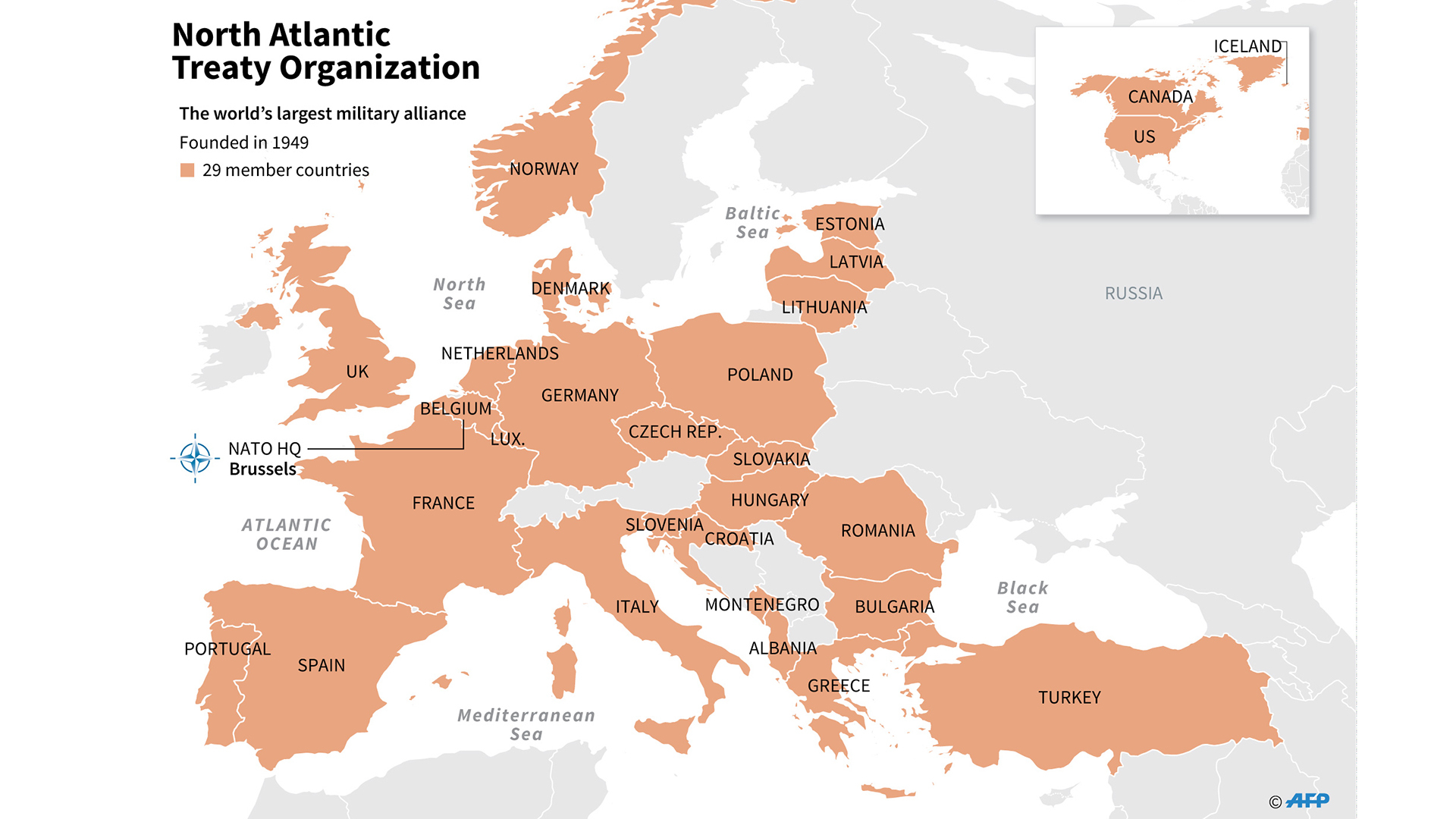
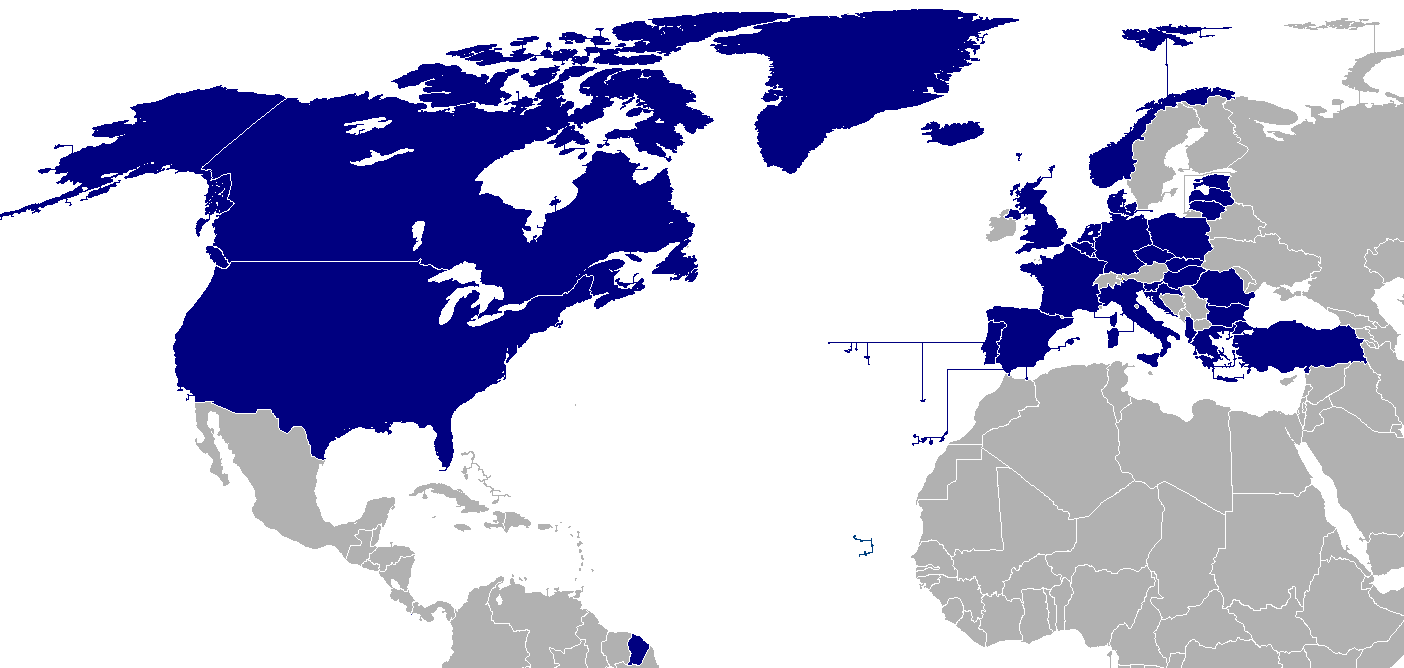
Nato members – NATO currently comprises 30 member countries from North America and Europe. The alliance’s membership has expanded significantly since its founding in 1949, reflecting the changing geopolitical landscape and the desire of nations to align with NATO’s collective security principles.
To join NATO, countries must meet specific criteria and undergo a rigorous accession process. The criteria include a commitment to democracy, individual liberty, and the rule of law; a willingness and ability to contribute to NATO’s collective defense; and compatibility with NATO’s military and political structures.
Decision-Making Process
NATO’s decision-making process is based on the principle of consensus, which means that all decisions must be agreed upon unanimously by all member states. The North Atlantic Council (NAC), composed of permanent representatives from each member country, serves as the primary decision-making body of the alliance. The NAC meets regularly at NATO headquarters in Brussels, Belgium, to discuss and vote on a wide range of issues related to NATO’s mission and operations.
NATO’s Role in International Security: Nato Members

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) plays a crucial role in maintaining international security and stability. Its collective defense commitment, peacekeeping operations, and cooperation with other organizations contribute significantly to global peace and security.
Collective Defense Commitment, Nato members
Article 5 of the Washington Treaty, the founding document of NATO, establishes a collective defense commitment among member states. This commitment obligates each member to come to the aid of any other member that is attacked. This principle of collective security ensures that an attack on one member is considered an attack on all, deterring potential aggressors and strengthening the security of member states.
Peacekeeping and Crisis Management Operations
NATO has actively participated in peacekeeping and crisis management operations worldwide. These operations have included missions in the Balkans, Afghanistan, and Libya. NATO’s involvement in these operations has helped stabilize conflict zones, prevent further escalation of violence, and facilitate humanitarian assistance.
Cooperation with Other Organizations
NATO cooperates closely with other international organizations, such as the United Nations and the European Union. This cooperation involves sharing information, coordinating operations, and providing mutual support. For instance, NATO has worked with the UN in peacekeeping missions and with the EU in counter-terrorism efforts.
As tensions escalate in the region, NATO members stand united in their commitment to collective security. President Biden’s recent visit to Brussels reaffirmed the alliance’s unwavering resolve, as outlined in the biden nato communique. The presence of all 30 NATO members underscores the strength and unity of the alliance, which remains a cornerstone of European security.
The recent Biden interview underscored the unwavering commitment of NATO members to collective defense. Biden emphasized the importance of unity among the allies, particularly in light of Russia’s aggression in Ukraine. The interview highlighted the critical role NATO plays in ensuring the security and stability of its member states.